Learn everything you need to know about trading Bank Nifty Index options, including key components, types, benefits, risks, and trading strategies and Bank Nifty top 10 weightage stocks
Introduction
The Bank Nifty Index, also known as the Nifty Bank, is a sectoral index comprising the top 12 most liquid and valuable stocks from the Indian banking sector. It is one of the most actively traded indices on the National Stock Exchange (NSE) of India. The Bank Nifty Index Option is a derivative contract that gives the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell the Bank Nifty Index at a predetermined price (strike price) on or before a certain date (expiry date).
Understanding Bank Nifty Index Option
Bank Nifty Index options are contracts that allow traders to speculate on the future direction of the Bank Nifty Index. The buyer of a call option has the right to buy the Bank Nifty Index at the strike price on or before the expiry date. If the index price is higher than the strike price at expiry, the buyer can exercise the option and make a profit. However, if the index price is lower than the strike price at expiry, the buyer can let the option expire and lose the premium paid.
The seller of a call option has the obligation to sell the Bank Nifty Index to the buyer at the strike price if the option is exercised. This means that the seller can lose money if the index price rises above the strike price. However, the seller can also make a profit if the index price falls below the strike price, as they will not have to deliver the shares.
Similarly, the buyer of a put option has the right to sell the Bank Nifty Index to the seller at the strike price on or before the expiry date. If the index price is lower than the strike price at expiry, the buyer can exercise the option and make a profit. However, if the index price is higher than the strike price at expiry, the buyer can let the option expire and lose the premium paid.
The seller of a put option has the obligation to buy the Bank Nifty Index from the buyer at the strike price if the option is exercised. This means that the seller can lose money if the index price falls below the strike price. However, the seller can also make a profit if the index price rises above the strike price, as they will not have to buy the shares. Key Components of Bank Nifty Index Options
- Strike Price: The strike price is the price at which the buyer has the right to buy or sell the Bank Nifty Index.
- Expiry Date: The expiry date is the date on or before which the option can be exercised.
- Premium: The premium is the price that the buyer pays to the seller for the option contract.
- Lot Size: The lot size is the minimum number of contracts that can be traded in a single transaction.
Bank Nifty weightage 2023
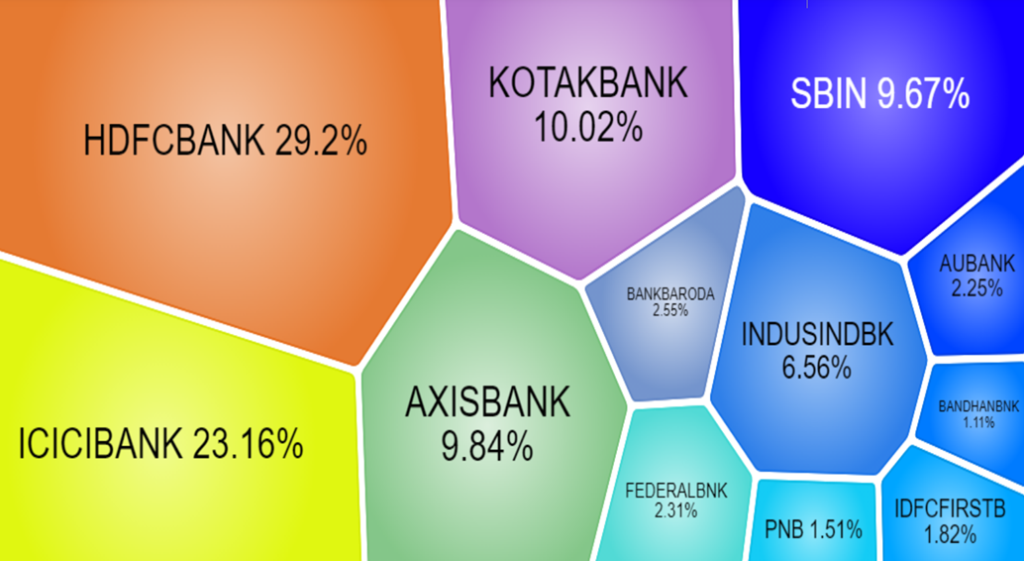
| Top constituents by weightage | |
| Company’s Name | Weight(%) |
| HDFC Bank Ltd. | 29.2 |
| ICICI Bank Ltd. | 23.16 |
| Kotak Mahindra Bank Ltd. | 10.02 |
| Axis Bank Ltd. | 9.84 |
| State Bank of India | 9.67 |
| IndusInd Bank Ltd. | 6.56 |
| Bank of Baroda | 2.55 |
| Federal Bank Ltd. | 2.31 |
| AU Small Finance Bank Ltd. | 2.25 |
| IDFC First Bank Ltd. | 1.82 |
Eligibility Criteria for Selection of Constituent Stocks:
- Companies should form part of Nifty 500 at the time of review. In case, the number of eligible stocks representing a particular sector within Nifty 500 falls below 10, then deficit number of stocks shall be selected from the universe of stocks ranked within top 800 based on both average daily turnover and average daily full market capitalisation based on previous six months period data used for index rebalancing of Nifty 500.
- Companies should form a part of the Banking sector.
- The company’s trading frequency should be at least 90% in the last six months.
- The Company should have a minimum listing history of 1 month as on the cut-off date.
- Companies that are allowed to trade in F&O segment are only eligible to be constituent of the index.
- Final selection of 12 companies shall be done based on the free-float market capitalization of the companies.
- Weightage of each stock in the index is calculated based on its free-float market capitalization such that no single stock shall be more than 33% and weightage of top 3 stocks cumulatively shall not be more than 62% at the time of rebalancing.
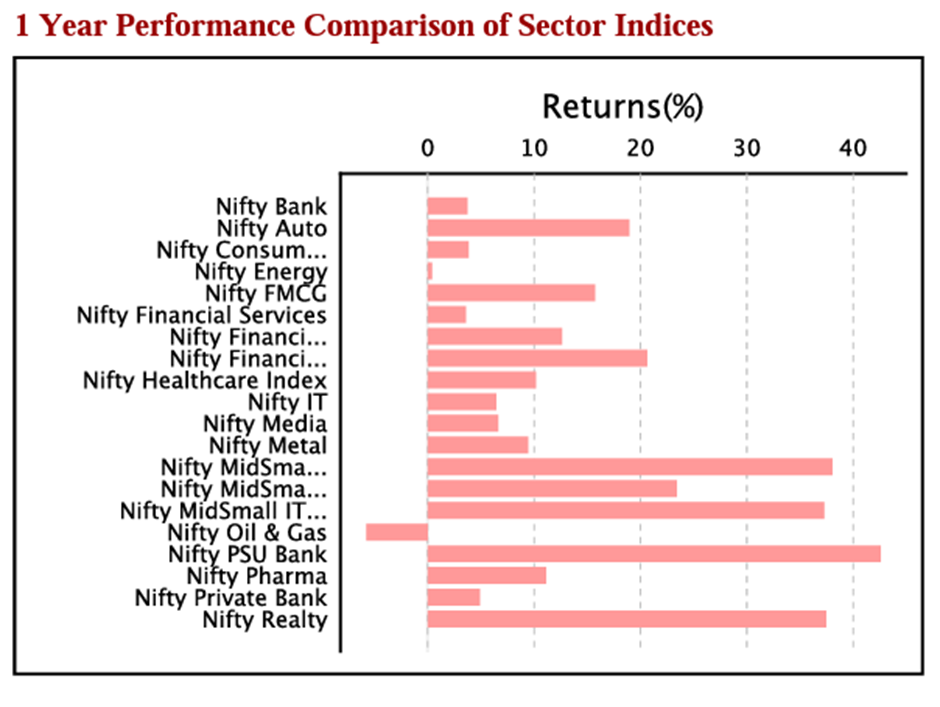
Bank Nifty Index vs. Another sectoral index as on Oct 2023.
Following are the ETF (Exchange traded fund) listed in India
| ISSUER NAME |
| Aditya Birla Sun Life Mutual Fund |
| AXIS Mutual Fund |
| HDFC Mutual Fund |
| ICICI Prudential Mutual Fund |
| Kotak Mahindra Mutual Fund |
| Mirae Asset Mutual Fund |
| Nippon India Mutual Fund |
| SBI Mutual Fund |
| UTI Mutual Fund |
Types of Bank Nifty Index Options
There are two main types of Bank Nifty Index options: call options and put options.
Call options give the buyer the right to buy the Bank Nifty Index at the strike price on or before the expiry date.
Put options give the buyer the right to sell the Bank Nifty Index at the strike price on or before the expiry date.
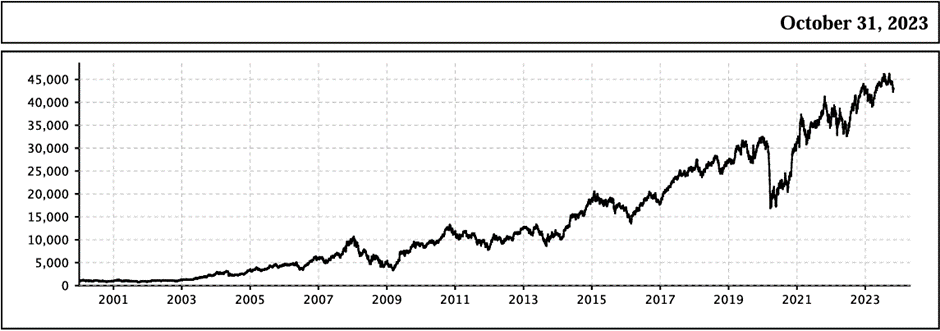
Bank Nifty Index historical data
Benefits of Trading Bank Nifty Index Options
There are several benefits to trading Bank Nifty Index options, including:
- Leverage: Options allow traders to control a large amount of the underlying asset with a relatively small amount of capital.
- Hedging: Options can be used to hedge against losses in other investments.
- Income generation: Options can be used to generate income through premium collection and writing covered calls.
- Speculation: Options can be used to speculate on the future direction of the market.
Risks of Trading Bank Nifty Index Options
There are also several risks to trading Bank Nifty Index options, including:
- Time Decay: The value of options decreases as the expiry date approaches.
- Volatility Risk: The value of options is more volatile than the value of the underlying asset.
- Unlimited Risk: The potential loss on a long call or put option is unlimited.
- Counterparty Risk: The seller of an option contract is at risk of loss if the buyer defaults on their obligation.
Bank Nifty Index trading tips/ Strategies
There are a number of different trading strategies that can be used with Bank Nifty Index options. Some of the most common strategies include:
- Covered Calls: A covered call strategy involves selling call options against a long position in the underlying asset.
- Protective Puts: A protective put strategy involves buying put options against a long position in the underlying asset.
- Straddles: A straddle strategy involves buying both a call and a put option with the same strike price and expiration date.
- Strangles: A strangle strategy involves buying both a call and a put option with different strike prices and the same expiration date.

