1 The Basics of Options
Options come in two primary forms:
- Call Options: These give the holder the right to buy the underlying asset at the strike price.
- Put Options: These give the holder the right to sell the underlying asset at the strike price.
2 Key Players in Options Trading
Options trading involves various participants, including:
- Buyer (Holder): The individual who purchases the option.
- Seller (Writer): The entity who creates and sells the option.
- Underlying Asset: The financial instrument upon which the option is based.
- Strike Price: The price at which the option holder can buy (for call options) or sell (for put options) the underlying asset.
- Expiration Date: The date on which the option contract expires.
3 What is Open Interest?
Open interest is a vital concept in the stock market, particularly when trading indices like Nifty and Bank Nifty. It represents the total number of outstanding contracts for a particular option or futures contract. In simpler terms, it reflects the total number of contracts that have not been settled or offset by an opposing trade.
4 How to Analyze Open Interest Data
To analyze open interest effectively, follow these steps:
- Identify Trends: Look for increasing or decreasing open interest, as it can indicate bullish or bearish sentiment.
| Call Open Interest | Put Open Interest | Trend |
| 10 lakhs | 7 lakhs | Down |
| 15 lakhs | 19 Lakhs | UP |
| 12 Lakhs | 12.50 Lakhs | Sideways |
| 25 lakhs | 26 lakhs | Sideways |
| 35 lakhs | 40 lakhs | UP |
| 47 lakhs | 32 lakhs | Down |
There should be meaning full difference between the open interest figures to identify the trend.
- Compare with Volume: Analyze open interest in conjunction with trading volume for more comprehensive insights.
- Expiry Dates: Pay attention to option expiry dates, as open interest often surges before expiration.
- Options Chain: Study the options chain to gauge the distribution of open interest across different strike prices.
5 Importance of Open Interest in Nifty and Bank Nifty
Open interest is critical in these indices for several reasons:
- Liquidity Indicator: Higher open interest typically means higher liquidity, making it easier to enter or exit positions.
- Price Predictions: Changes in open interest can signal potential price movements.
- Options Strategies: It is fundamental for options traders who employ various strategies like covered calls and straddles & straggle. We will write separate article on this topic for brief understanding.
6 Trading Strategies Using Open Interest
Implement these strategies to leverage open interest data:
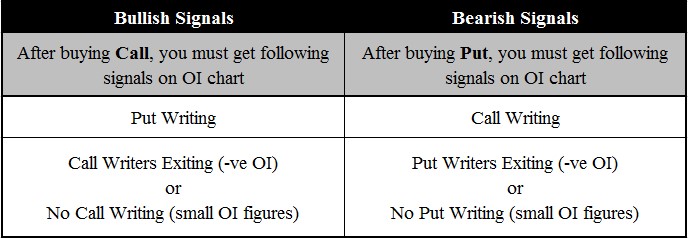
- Bullish Trends: Consider buying when open interest increases alongside rising prices.
- Bearish Trends: Look for opportunities to short when open interest rises while prices fall.
- Range-Bound Markets: In choppy markets, focus on changes in open interest to identify potential breakouts.
- Option Writing: Write options when open interest is high and market volatility is low.
7 Open Interest vs. Volume
While open interest and trading volume are related, they serve different purposes:
- Open Interest: Reflects the number of open contracts, indicating the potential for future trading activity.
- Volume: Represents the number of contracts traded in a specific time frame, showing current market activity.
In conclusion, mastering open interest in Nifty and Bank Nifty can significantly enhance your trading prowess. By understanding its dynamics and integrating it into your trading strategy, you can make more informed decisions and achieve greater success in the stock market.
